What is Zilla?
What is Zilla?
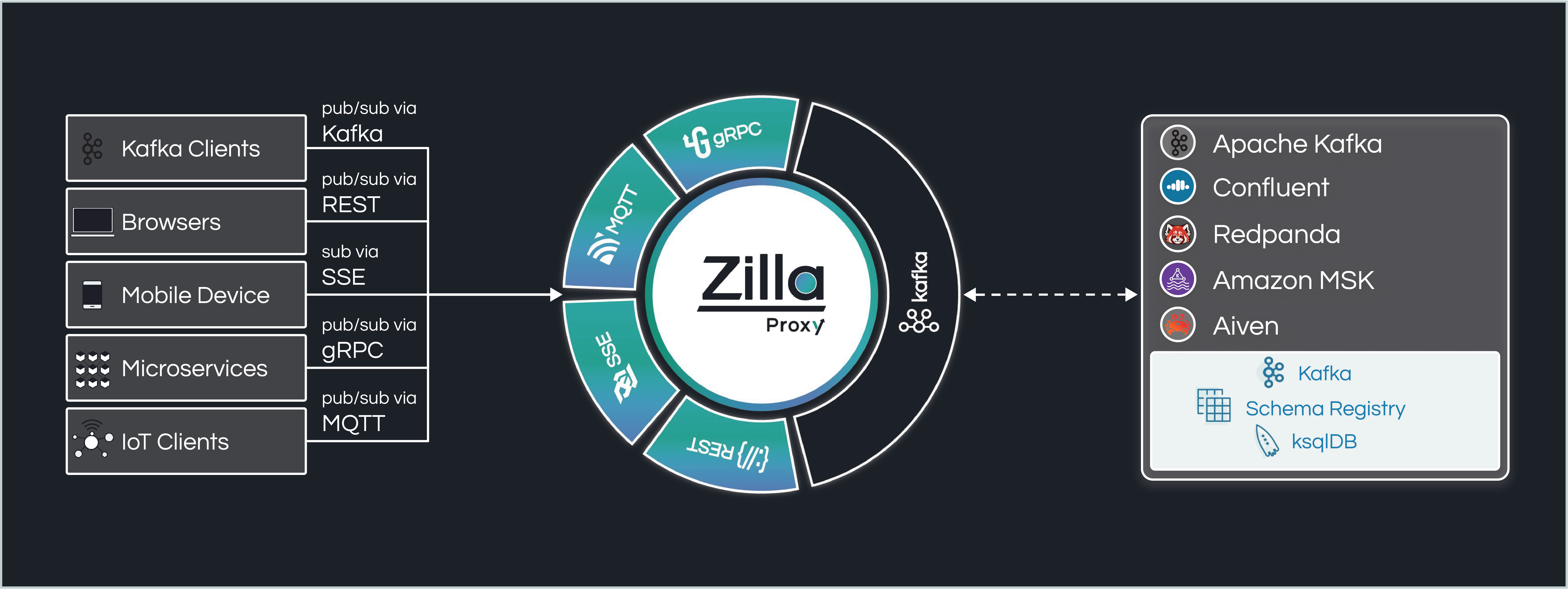
Zilla is a multi-protocol edge and service proxy that helps streamline, secure, and manage event-driven architectures. It is meant to be deployed alongside event-driven applications and services to enforce authentication, validate schemas, gather metrics, and terminate TLS. Additionally, Zilla has advanced protocol meditation capabilities, particularly to and from Kafka.
Zilla is stateless, cloud-native, and supports various network and application protocols, including HTTP, Kafka, SSE, MQTT, gRPC, and WebSocket (additional protocols are on the way).
Just want to build?
Jump to the quickstart guide.
Why Zilla?
Some of the hardest operational challenges inside distributed architectures relate to networking and observability. As a result, edge and service proxies are required to achieve resilient, transparent, and properly routed connectivity among distributed services.
While solutions such as Envoy, HAProxy, NGINX, etc. can help unify a distributed data plane, they are designed for “mesh” deployments in which services are directly interconnected and communicate almost exclusively over HTTP. Inside event-driven architectures (EDAs) though, services are separated by an event/message broker, and multiple protocols are present. This decoupled and multi-protocol nature of EDAs presents a new class of networking, observability, and security challenges that the Zilla proxy is designed to address.
Zilla Features
Self-Contained, Stateless Architecture
Zilla has no external dependencies, is stateless, and is highly memory efficient. When deployed as an edge proxy, it scales horizontally to support millions of concurrently connected clients.
HTTP/2, gRPC, SSE, MQTT, and Kafka Support + Protocol Mapping
Inside Zilla, every protocol, whether it is TCP, TLS, HTTP, Kafka, gRPC, etc., is treated as a stream, so mapping between protocols simplifies to mapping protocol-specific metadata.
Protobuf, Avro, and JSON Schema payloads
Zilla supports payload schema specifications for message validation and translation.
OpenAPI and AsyncAPI Support
Zilla supports different API schema specifications for message validation and API creation.
API Registry and Schema Registry Integrations
Zilla integrates with schema registries and API registries including Apicurio, Confluent Schema Registry in Zilla, and Karapace.
Security
Zilla can terminate TLS and supports JWT-based authorization for REST, SSE, and MQTT endpoints/services.
Observability
Zilla can expose a Prometheus metrics endpoint and logs events to stdout. Additionally Zilla supports OpenTelemetry for both metrics and logging and. Syslog and AWS Cloudwatch are supported in Zilla.
Zilla Use Cases
Zilla can be used as a service proxy (sidecar) or as an AsyncAPI Kafka gateway.
Service Proxy
When deployed in front of an existing HTTP, SSE (Server Sent Events), MQTT, Kafka, or gRPC service, Zilla adds metrics, logging, message validation, and authentication.
For HTTP Services
- Gather metrics and telemetry data on traffic flowing in and out of an HTTP service.
- Add JWT-based client authentication.
- Enforce OpenAPI and AsyncAPI schema definitions and reject invalid requests.
For SSE Services
- Gather metrics and telemetry data on traffic flowing out of an SSE service.
- Add JWT-based client authentication with Continuous Authorization. Zilla supports Continuous Authorization which gracefully re-authorizes a client on an SSE server’s behalf, without abruptly terminating message streams.
- Enforce AsyncAPI schema definitions and reject invalid outbound messages.
For MQTT Services
- Gather metrics and telemetry data on traffic flowing in and out of an MQTT service.
- Add JWT-based client authentication.
- Enforce AsyncAPI schema definitions and reject invalid inbound messages.
For Kafka Services
- Gather metrics and telemetry data on traffic flowing in and out of a Kafka service in Zilla.
For gRPC Services
- Gather metrics and telemetry data on traffic flowing in and out of a gRPC service.
- Enforce Protobuf schema definitions and reject invalid inbound messages.
AsyncAPI Kafka Gateway
Zilla can abstract Apache Kafka for web applications, IoT clients, and non-Kafka microservices. With Zilla, OpenAPI and AsyncAPI definitions can be mapped to Kafka, enabling Kafka topics to be exposed over user-defined REST, SSE, MQTT, and gRPC APIs.
Zilla has no external dependencies and does not rely on the Kafka Consumer/Producer API or Kafka Connect. Instead, it natively supports the Kafka wire protocol and uses novel protocol mapping techniques to establish stateless API entry points into Kafka. As a gateway, Zilla also addresses security enforcement, observability, and connection offloading on the data path.
Kafka Fan-Out to Web and IoT (Data Broadcasting)
Broadcast data from Kafka to millions of clients over SSE, MQTT, and gRPC. With Kafka and Zilla real-time updates such as stock tickers, sports scores, logistics trackers, and push notifications can be reliably delivered to end users and systems at scale. Kafka is not designed to support a large number of connected clients, so besides protocol mapping, Zilla also handles connection offloading, by pushing data out of a real-time cache. This local cache is synchronized with Kafka for specific topics through a small number of connections, independent of the number of connected clients. The cache also indexes message keys and headers upon retrieval from Kafka, supporting efficiently filtered reads from cached topics.
Kafka Fan-In from Web and IoT (Clickstream and Telemetry Ingestion)
Ingest data into Kafka from millions of clients over HTTP, MQTT, and gRPC. With Kafka and Zilla, clickstream and telemetry data can be processed and responded to in real time. Kafka is not designed to support a large number of connected clients, so besides protocol mapping, Zilla also pools connections, ensuring the number of inbound connections is independent of the number of connected clients.
IoT Ingestion and Control
Remove an MQTT broker from a Kafka-based EDA to streamline an IoT deployment. Zilla can persist MQTT messages and client states across pre-configured Kafka topics. Once these messages are in Kafka, they become readily available to Kafka clients, consumers, and stream processing pipelines. Zilla works bidirectionally, so data can be forwarded back to MQTT clients from Kafka producers.
Event Mesh
Interface REST or gRPC service meshes to an event-driven architecture for an event mesh deployment. Achieve CQRS, request-response over messaging, and event-sourcing design patterns.
Secure Public Access (Zilla Plus)
Route connectivity between Kafka clients and privately networked Kafka brokers. With Zilla, external and third-party Kafka clients can securely connect, publish messages, and subscribe to topics in a remote, private cluster.
Zilla Benefits
Zilla helps streamline, secure, and manage event-driven architectures. As an AnsycAPI Kafka gateway, it replaces custom code, Kafka Connect®, MQTT brokers, and other integration middleware. With Zilla, teams save time, reduce DevOps burden, and remove complexity from their architectures.
Who Zilla is for?
- Data platform/Kafka integration engineers who are tasked with reliably, securely, and accessibly exposing a Kafka cluster to internal and/or external teams.
- Application developers who do not have Kafka expertise but want/need to build applications on top of real-time data streams.
- API architects who want to drive business functionality via their AsyncAPI schemas.
Zilla Plus
Zilla is made available under the Aklivity Community License. This open-source license gives the freedom to deploy, modify, and run Zilla as needed, as long as it is not turned into a standalone commercialized “Zilla-as-a-service” offering. Running Zilla in the cloud for any workload, whether production or not, is fine.
A commercial version of Zilla ( Zilla “Zilla Plus”) is available, which includes additional enterprise integrations and support. Secure Public Access is a Zilla-only supported use case. For more information, please visit the Zilla product page.

