Aiven
Aiven
This is how to connect to Aiven Kafka from Zilla. The examples use the below Environment variables.
| Environment variable | Description |
|---|---|
TRUSTORE_PATH | The path to the truststore that stores CA cert that you want to trust. |
TRUSTORE_TYPE | Keystore types such as pkcs12, jceks, and etc |
TRUSTORE_PASSWORD | Truststore password. |
KEYSTORE_PATH | The path to the keystore that stores access key. |
KEYSTORE_TYPE | Keystore types such as pkcs12, jceks, and etc |
KEYSTORE_PASSWORD | Keystore password. |
CA_CERT_ALIAS | Unique string that identifies the certificate entry in the truststore. |
SIGNED_CLIENT_CERT_ALIAS | A unique string that identifies the key cert entry chain in the keystore |
BOOTSTRAP_SERVER_HOSTNAME | Target Kafka hostname |
BOOTSTRAP_SERVER_PORT | Target Kafka port number |
Aiven Parameters
The Aiven Kafka requires clients to connect via TLS mutual authentication and provides the following files Client Key, Client Certificate, and CA Certificate to achieve that. You can download them by going to Aiven Console -> Kafka Cluster -> Overview Tab as shown below.
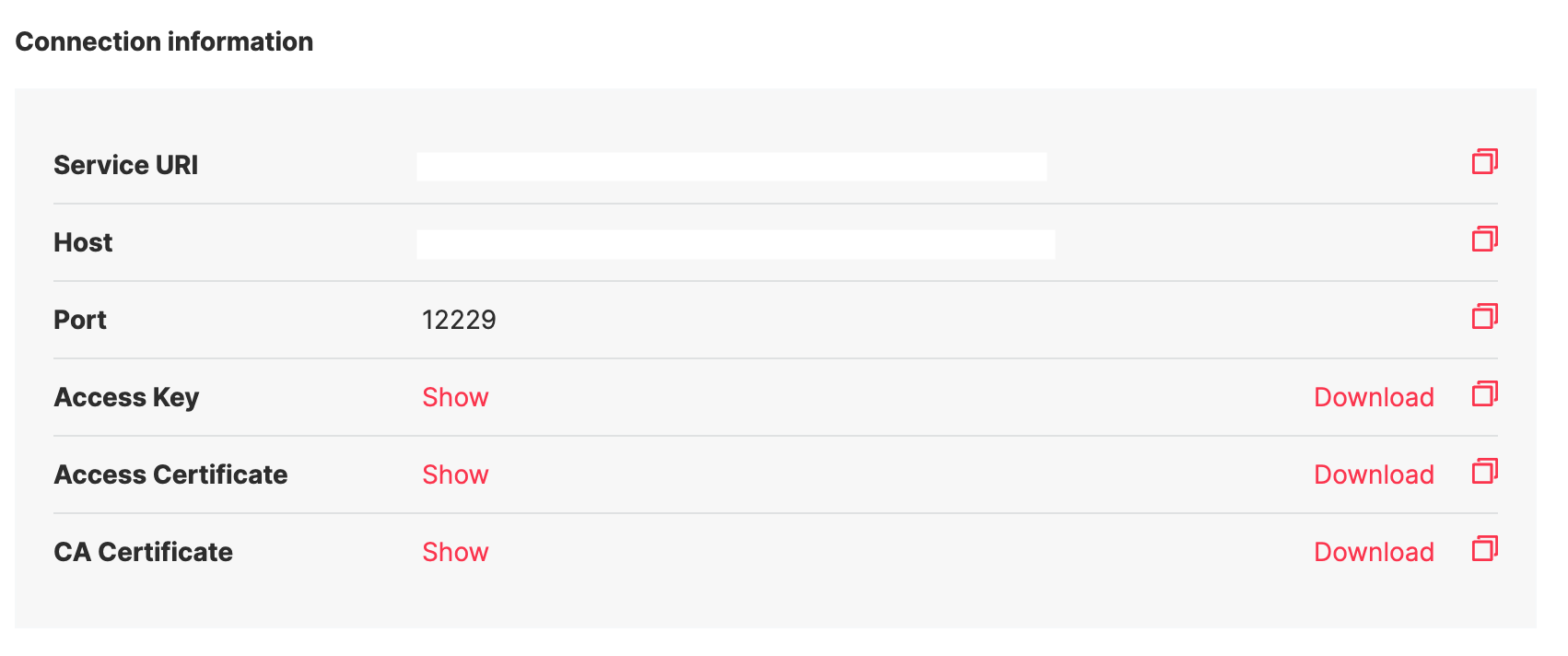
you should have the following files:
service.key- Access Keyservice.cert- Access Certificateca.pem- CA Certificate
The next step is to generate the truststore and keystore.
truststore.p12- contains the trusted server certificates or certificate authoritieskeystore.p12- contains the signed client certificates
You can use the scripts shown below to generate truststore.p12 and keystore.p12 files using certificates and keys downloaded from Aiven Kafka Console. Please replace all caps lock words.
keytool -import -file ca.pem \
-alias YOUR_KAFKA_SIGNED_CLIENT_CERT_ALIAS \
-keystore truststore.p12openssl pkcs12 -export -in service.cert -inkey service.key \
-out keystore.p12 -name YOUR_KAFKA_CA_CERT_ALIAS \
-CAfile ca.pemConfigure Zilla
And the final step is to configure a vault with truststore and keystore, then reference the vault in the south_tls_client binding.
vaults:
client_vault:
type: filesystem
options:
trust:
store: ${{env.TRUSTORE_PATH}}
type: ${{env.TRUSTORE_TYPE}}
password: ${{env.TRUSTORE_PASSWORD}}
keys:
store: ${{env.KEYSTORE_PATH}}
type: ${{env.KEYSTORE_TYPE}}
password: ${{env.KEYSTORE_PASSWORD}}
bindings:
...
south_kafka_client:
type: kafka
kind: client
options:
servers:
- ${{env.KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVER}}
exit: south_tls_client
south_tls_client:
type: tls
kind: client
vault: client_vault
options:
trust:
- ${{env.CA_CERT_ALIAS}}
keys:
- ${{env.SIGNED_CLIENT_CERT_ALIAS}}
exit: south_tcp_client
south_tcp_client:
type: tcp
kind: clientNOTE
SNI adds the domain name to the TLS handshake process so that the Zilla process reaches the right domain name and receives the correct SSL certificate.
To test the above config you can use it to add or replace the necessary bindings in the http.kafka.sasl.scram example.

